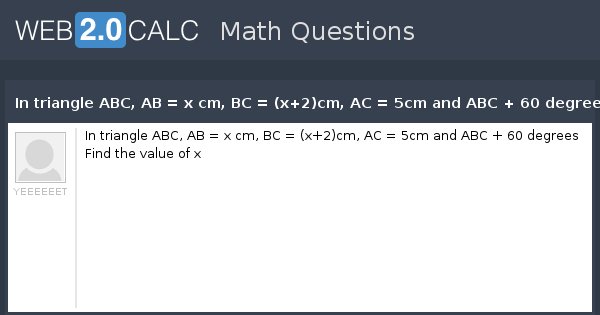
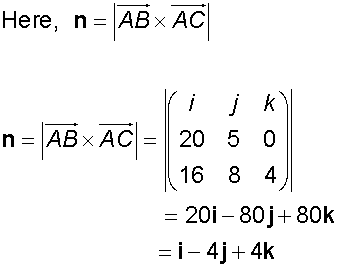Solved: 198.In Delta ABC AB=x , BC is three more than AB , and AC is twice BC. If the perimeter of [geometry]

in triangle ABC AB=x AC=7 and angle B=90° cosB= 0 evaluate √7-x tanC+√7+x cotA-14 cosA+21 sinC +√49+x² cosB - Brainly.in

The semi-lattice X ¼ fa, b, c, d, ab, ac, ad, bc, bd, cd, abc, abd,... | Download Scientific Diagram

If the roots of the equation (c2 – ab) x2 + 2(bc- a2 ) x+ (b2 – ac) = 0 are equal , then prove that either a = 0 or a3 + b3 + c3 = 3abc.
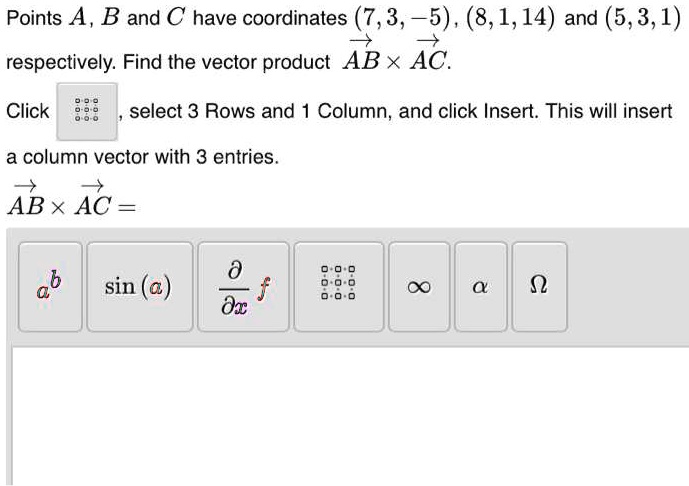
SOLVED: Points A, B and C have coordinates (7,3, 5) , (8,1,14) and (5,3,1) respectively: Find the vector product AB x AC. Click 33 select 3 Rows and 1 Column, and click

Allen Bradley Guardmaster 440G-T27127 mágnestekercses reteszelő kapcsoló, M20, 24 V AC/DC, Műanyag burkolat, IP67, 39 x | RS
If a, b, c are real, then f(x) = |((x + a^2), ab, ac), (ab, x + b^2, bc), ( ac, bc, x + c^2)| is decreasing in - Sarthaks eConnect | Largest Online Education Community

In triangle ABC, Angle ACB=90°, seg CD is perpendicular to seg AB, seg DE is perpendicular to seg CD. Show that: CD² x AC = AD x AB x DE.

If AB = x +3, BC =2 x and AC =4 x 5, then what will be the measure of x, if B lies on AC ?A. x= 1B. x= 4C. x=10D. x=8

a) Define vector product (b) Understand the properties of vector product (c)Find the area of parallelogram. - ppt download
If a, b, c are real numbers, find the intervals in which f(x) = |(x + a^2, ab, ac), (ab, x + b^2, bc), (ac, bc, x + c^2)| - Sarthaks eConnect

In triangle ABC, Angle ACB=90°, seg CD is perpendicular to seg AB, seg DE is perpendicular to seg CD. Show that: CD² x AC = AD x AB x DE.